TNPSC Field Surveyor FS & Draftsman Recruitment Syllabus 2022
Organisation : Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission TNPSC
Post Name : TNPSC Field Surveyor FS & Draftsman Recruitment 2022
Services : Tamil Nadu Survey and Land Records Subordinate Service & Tamil Nadu Town and Country Planning Subordinate Service
Announcement : TNPSC Field Surveyor FS & Draftsman Recruitment Syllabus 2022
Qualification : Diploma
Number of Vacancies : 1089
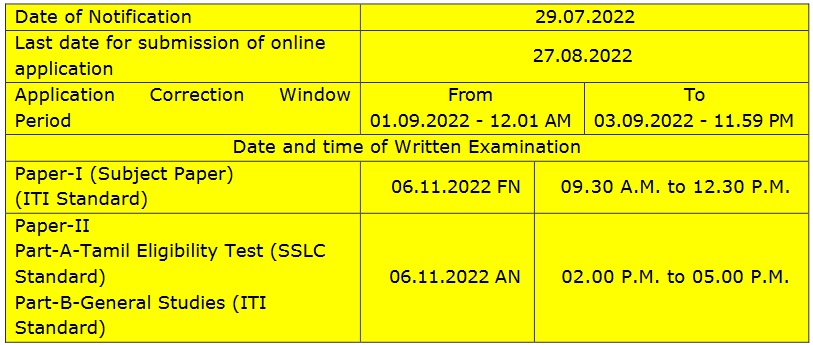
Starting Date : 29th July, 2022
Last Date : 27th August, 2022
Exam Date : 06th November, 2022
Website : https://www.tnpsc.gov.in/English/Notification.aspx
What is TNPSC FS & Draftsman Recruitment?
TNPSC Field Surveyor FS & Draftsman Recruitment is Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission TNPSC. A Diploma in Civil Engineering from any Institute approved by All India Council for Technical Education. Applications are invited only through online mode upto 27.08.2022 for direct recruitment to the posts of Field Surveyor and Draftsman included in Tamil Nadu Survey and Land Records Subordinate Service and Surveyor-cum-Assistant Draughtsman in Tamil Nadu Town and Country Planning Subordinate Service. The last date of submission is 27th August, 2022.

Syllabus For TNPSC FS & Draftsman Exam
The Syllabus For TNPSC FS & Draftsman Exam are given below,
Paper-I (Objective Type)
Unit-1: Basic Engineering Drawing
Role of Surveyor:
Know about the role of a surveyor – State the importance of survey.
Layout of drawing sheets and title block:
State the measuring of the term ‘Layout’ of drawing sheet – List the different
layout styles of drawing sheets – Explain margin, frame, title block etc.
Free hand sketching:
State the need free hand sketching – List the situations wherein free hand
sketching is useful.
Drawing equipment – Drawing board, T-Square:
State the construction and use of drawing boards and ‘T’ square – State the
standard sizes of drawing board as per IS:1444-1989 – State the standard sizes of
‘T’ square as per IS: 1360-1989 – State the construction and uses of drafting
machine – Select the pencil grades for different drawing application – Select the
purpose of erasing shield – State the use of set squares in drawing work.
Folding of sheets:
Explain the method of folding in different size of drawing sheets.
Lettering styles:
Recognise different lettering styles – Designate the letters and numerals as per IS
norms – State standard properties for height, width and spacing of letters.
Scales:
State the necessity of scales – Explain representative fraction (RF) – List the types
of scales – Explain plain, Diagonal scale, comparative scale and Vernier scale.
Dimensioning:
Explain the types of dimensioning – Explain the elements of dimensioning –
Explain the methods of indicating dimensioning – Explain the arrangement of
dimensioning.
Types of lines and angles:
Define points and lines – State classification of lines – State the different types of
angles – Explain the method of measuring angles.
Triangles and their properties:
Define triangles – Name the different types of triangles and state their properties.
Quadrilaterals and their properties:
Define a quadrilateral – Name the quadrilaterals – State the properties of
quadrilaterals.
Polygon and their properties:
Define a Polygon – Name the Polygon in terms of the number of sides – State the
properties of Polygon.
Unit-2: Chain Surveying
Introduction about Surveying:
Define Surveying – State the object of surveying – State technical terms – State the
classification of Surveying – State the principles of Surveying – State the work of
Surveyor – State the accuracy in chain Survey – State steel band
Measurement of distance by a chain and chaining:
State the methods of determining distance – State chaining and chaining a line –
State unfolding the chain – Describe the reading the chain – State folding the
chain – Calculate the errors in chaining.
Introduction about chain survey instruments:
State the construction and uses of the following chain survey instruments.
Ranging:
State ranging – State the necessity of ranging – State the types of ranging –
Interpret the signals surveyor and the corresponding action by assistance.
Chaining on sloping ground:
Explain the methods of changing on sloping ground – State necessity of
calculating horizontal distances.
Offset and Offsetting:
State the meaning of offset and offsetting – State the classification of offsets, its
limits and its definition – State the methods of taking offsets for various site
conditions.
Obstacles in chain surveying:
Define obstacles – State the three types of obstacles – Calculate the obstructed
distance.
Introduction used for setting out right angles:
List out the instrument used for setting out right angles – State the types of cross
staff and optical square – State the construction of cross staff and optical square –
Explain the principles of optical square – State the uses of cross staff and optical
square.
Introduction about triangulation survey:
Define the triangulation and traverse in survey – State closed and open traversed
survey – State the three types of survey lines in triangulation
Explain about field work.
Calculation of area:
Calculate the areas of an irregular field – Apply geometrical formula for
calculating the area – Describe the construction and use of planimeter.
Unit – 3: Compass Surveying
Identification and parts of instruments in compass survey:
State about traversing – State types of compass – Name the prismatic compass
and construction – Construction of surveyor’s compass Determining the bearing of a given triangular plot ABC and calculation of included angles: Calculate angles from bearings – Calculate bearing from angles. Determining the bearing of a given pentagonal plot of ABCDE and calculating included angles magnetic declination and plotting of compass
survey:
Calculate the angles from bearing for a closed traverse – Calculate the bearing
from angles for a closed traverse – Calculate the bearing of a pentagon – Define
the dip of the magnetic needles – State the magnetic declination and variations –
Calculate true bearing – State local attraction and its elimination – Explain about
errors and its limits – State the testing the prismatic compass.
Unit – 4:Plane Table Surveying
Setting up of plane table and methods of plane tabling:
State plane tabling – Name the instruments and accessories used in plane tabling
– State the construction and uses of instruments accessories of plane tabling –
Explain about the setting up of plane table over a station – Explain about leveling,
centering and orientation in plane tabling – Explain the methods of plane tabling
Methods of plane table survey:
Methods of plane table survey – Radiation methods of plane table survey
Intersection methods of plane table survey
Traversing method of plane table survey:
State traverse methods of plane table survey – Conduct traverse methods of plane
table survey.
Locate and plot new building by two point and three point problem: Define
about resection – State two and three point problem – Describe Lehman’s rule –
List out the errors in plane tabling – Describe the advantage and disadvantage
Prepare a road map for 1/2 km showing details on both sides:
Prepare a road map and locate the details on both sides
Inking, finishing, colouring and tracing of plane table map:
Explain about colouring of surveying symbols – Explain the importance of tracing
– State the techniques/order of tracing a drawing – State the different types of
reproduction of drawings.
Minor instruments used with or without plane tabling:
Explain about the construction and uses of Abney level, tangent clinometers, De
Lisel’s clinometers.
Syllabus Link : http://www.syllabus.gen.in/uploads/pdf2022/3738-note.pdf
Unit – 5: LEVELLING&CONTOURING
Instruments Used for Levelling:
Explain the tilting level and auto level – Explain the construction a dumpy level –
Explain the classification of leveling staff.
Introduction of contouring:
Define contouring – Explain the terms in contouring – Narrate the characteristics of contour
Topography and contour:
State Topography – State contour.
Tracing of grade contour:
Trace the contour gradient for alignment of roads, railways, etc –
Determine the volume of earth work and capacity of reservoir
Computation of volume:
Explain the various methods for the quantity of earth work – Compute quantity of
earth work by average depth method – Compute the quantity of earth work by
trapezoidal and primordial formula
Unit-6:THEODOLITE
Introduction to theodolite:
Explain the uses of the theodolite – Explain the classify of the theodolite – Explain
the designate of the theodolite
Temporary adjustment of theodolite:
Set up and perform centering of the instrument – Level up the theodolite
Eliminate parallax
Measuring horizontal angle-repetition method:
Explain the repetition method – Stage advantage of repetition method
State errors which are not eliminated by repetition method.
Measuring vertical angle:
Define vertical angle – Differentiate angle of elevation and angle of depression –
Explain how to measure vertical angle
Deflection angle and direct angle:
State deflection angle – Differentiate right deflection angle and left deflection angle
– State the direct angle – Differentiate deflection angle and direct angle
Prolonging a line:
State the method for prolonging a line – Compare the method for prolonging a line
– State most suitable method for prolonging a line
Intersection of two straight lines:
Explain method one: to find intersection point of two lines – Explain method two:
to find intersection point of two lines
Laying of a horizontal angle:
Explain laying of a horizontal angle by ordinary method – Explain laying of a
horizontal angle by repetition method – Find equivalent lenier distance for an
angular value
Traverse:
State uses of traverse surveying – State types of traverse – Differentiate open end
closed traverse
Traverse checking:
Explain the checks for open traverse – Explain the checks for closed traverse
What are the important date of TNPSC FS & Draftsman Exam?
The important date of TNPSC FS & Draftsman Exam are given below,